"Chemistry Explained." Chemistry Explained. N.p., n.d. Web. 28 Oct. 2015.
Introduction:
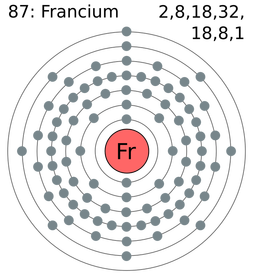
Francium’s symbol is Fr. The atomic number, which is how many electrons and protons there are, is 87 each. The atomic mass is 223. 223 is the sum of protons and neutrons. So there are 87 protons and 136 neutrons. The 87 electrons are split up between seven energy levels. But they are not split evenly. There are two electrons on the first, eight on the second, 18 on the third, 32 on the fourth, 18 on the fifth, eight on the sixth, and only one on the seventh.
History of Francium:
Unfortunately, the world does not know much about Francium. Even after the discovery of Francium in 1939, scientists are still working on studying it. Marguerite Perey from the Curie Institute in Paris was the first person ever to discover Francium. Obviously, Francium was named after the country, France. Francium has not been found without being connected to another element.
Abundance of Francium:
|
No more than 30g of Francium has been on Earth at one time. It is actually the second-most rarest element on the entire periodic table. Francium’s isotopes range from 200 to 232. Overall, we know of 33 known isotopes. None of them are stable. Here are some of them:
Francium-223 is the element’s longest lived isotope. It has a half-life of 22 minutes. (About the time it is to cook a pizza) Francium-212 has a half-life of 19 minutes. Francium-221 has a half-life of 5 minutes. Francium-216 has a half-life of 0.7 microseconds. |
Francium in Technology:
Francium has no uses in technology because it is extremely reactive, rare, and is currently being studied.
How Reactive is Francium?
|
Francium is the most reactive metal on the entire periodic table. Unfortunately, since it is so rare, no one can purchase it or retrieve any in large quantities. Because of its similar properties to cesium and sodium, it is extremely reactive. It is extremely radioactive as well the most unstable of the first 101 elements. Francium occurs naturally because of the radioactive decay of the element, actinium. Some interesting compounds of Francium are Francium Sulfide, Francium Fluoride, Francium Bromide, Francium Acetate, or even Francium Hydrogen Oxalate. That's a mouthful. Try saying that five times fast!
|
Interesting Facts:
Francium completed man’s discovery of naturally occurring elements. It is the most radioactive and reactive of the Alkali metals. Francium has the least electronegativity of all the elements. Francium is currently being studied at Stony Brook University, New York. At that university, scientists contain about ten thousand francium atoms at one time using laser beams in a magnetic field to measure their properties.
Sources:
"Chemistry Explained." Chemistry Explained. N.p., n.d. Web. 28 Oct. 2015.
"The Photographic Periodic Table of the Elements." The Photographic Periodic Table of the Elements. N.p., n.d. Web. 28 Oct. 2015.
"Main Page." Wikimedia Commons. N.p., n.d. Web. 28 Oct. 2015.
"ENDMEMO." Common Compounds of Francium Fr. N.p., 2015. Web. 28 Oct. 2015.
"Francium Element Facts." Chemicool. N.p., n.d. Web. 28 Oct. 2015.
Knapp, Brian. "Francium." Francium to Polonium. Vol. 17. Danbury: CT, 2002. 4. Print. The Elements.
Green, Dan. "Alkali Metals." The Elements: The Building Blocks of the Universe. New York, NY: Scholastic, 2012. 30. Print.
"The Photographic Periodic Table of the Elements." The Photographic Periodic Table of the Elements. N.p., n.d. Web. 28 Oct. 2015.
"Main Page." Wikimedia Commons. N.p., n.d. Web. 28 Oct. 2015.
"ENDMEMO." Common Compounds of Francium Fr. N.p., 2015. Web. 28 Oct. 2015.
"Francium Element Facts." Chemicool. N.p., n.d. Web. 28 Oct. 2015.
Knapp, Brian. "Francium." Francium to Polonium. Vol. 17. Danbury: CT, 2002. 4. Print. The Elements.
Green, Dan. "Alkali Metals." The Elements: The Building Blocks of the Universe. New York, NY: Scholastic, 2012. 30. Print.
Page created by G. Rogers